Surplus inventory is an apocalypse faced by businesses every now and then. Effective inventory management is crucial for maintaining profit and operational efficiency. Surplus inventory in general hinders capital flow, increases storage costs, and leads to obsolescence. This article explores innovative approaches to surplus inventory control, offering fresh perspectives and cutting-edge strategies for businesses looking to optimize their inventory management practices.
What is Excess Inventory?
Excess inventory is surplus stock that is beyond the market demands or what a company is expected to sell or used in a required time. This excess tie up capital, takes up storage space, and may lead to additional costs or losses. Excess inventory can cause huge loss if not properly regulated and many companies to earn a minimum amount rather than total loss prefers innovative ways to consume them. Many businesses utilize industrial surplus distributors to consign surplus inventory and recoup potential financial losses.
Causes of Excess Inventory:
- Inaccurate Demand Forecasting: Poor predictions of future sales can lead to overordering.
- Bulk Discounts: Companies may over-purchase to take advantage of volume discounts.
- Seasonal Products: Misjudging seasonal product sales can result in overstocking.
- Poor Inventory Management: Inefficient tracking and reordering processes can cause overbuying.
- Changes in Market Conditions: Unexpected shifts in consumer behavior can reduce demand.
How to Manage Excess Inventory?

There are many ways to control and manage excess inventory but, in 2024 where technology is in the forefront of every work field it is sensible to harness innovative ideas.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is essential for any business to manage their inventory effectively. It predicts future demands based on the current trends, market demands, history of the company’s sales and season-based product with data driven predictions.
Key benefits:
- Improved forecast accuracy
- Reduction in overstocking
- Better allocation of resources
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The Economic Order Quantity model is a classic inventory control technique that helps determine the optimal order quantity to minimize total inventory costs.
How it works:
- Calculates the ideal order quantity by balancing ordering costs and holding costs
- Assumes constant demand and fixed costs
Formula: EOQ = sqrt((2 * D * S) / H)
Where: D = Annual demand
S = Fixed cost per order
H = Annual holding cost per unit
Benefits:
- Minimizes total inventory costs
- Provides a straightforward approach to inventory management
- Useful for items with stable demand
ABC Analysis
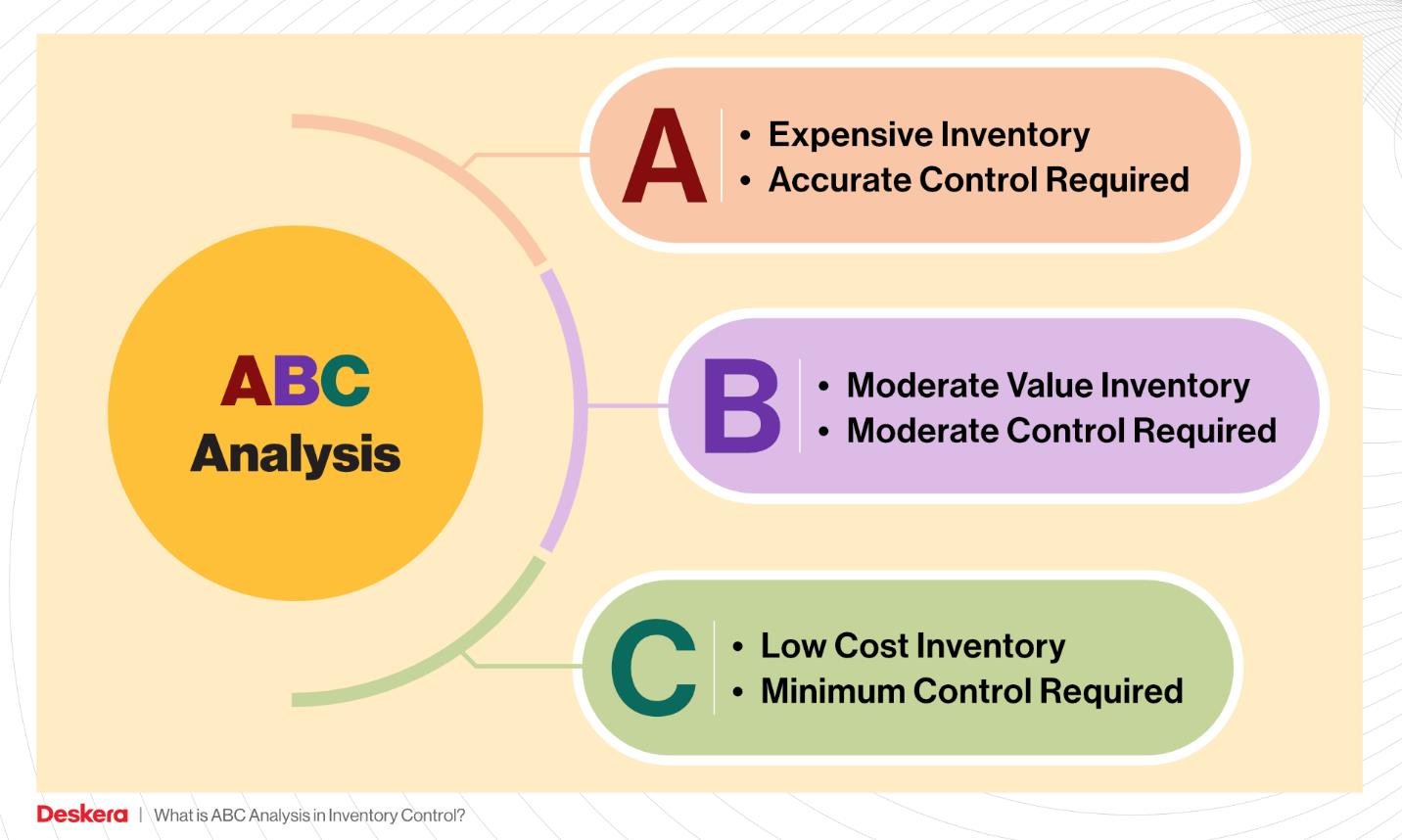
ABC Analysis is a method of categorizing inventory items based on their importance and value to the business.
Categories:
- A items: High-value products with low sales frequency
- B items: Moderate value and sales frequency
- C items: Low-value products with high sales frequency
Implementation:
- Calculate the annual consumption value for each item
- Sort items in descending order of annual consumption value
- Calculate cumulative annual consumption value and percentage
- Assign categories based on predetermined thresholds
Benefits:
- Focuses attention on high-value items
- Allows for tailored inventory control strategies for each category
- Improves resource allocation
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
Vendor-Managed Inventory is a collaborative approach where the supplier takes responsibility for maintaining the retailer’s inventory levels.
Key features:
- Supplier monitors retailer’s inventory levels
- Supplier initiates orders based on predetermined criteria
- Increased data sharing between supplier and retailer
Benefits:
- Reduces stockouts and overstocking
- Lowers ordering and holding costs for the retailer
- Improves supplier-retailer relationships
Challenges:
- Requires trust and information sharing between parties
- May lead to dependency on suppliers
- Requires sophisticated inventory tracking systems
Min-Max Inventory Method
The Min-Max method involves setting minimum and maximum inventory levels for each item and replenishing stock when it falls below the minimum level.
How it works:
- Set minimum inventory level (reorder point)
- Set maximum inventory level
- Monitor inventory levels continuously
- Place an order when stock falls below the minimum level
- Order quantity = Maximum level – Current stock level
Benefits:
- Prevents stockouts and overstocking
- Simple to implement and understand
- Adaptable to different types of inventory items
Dropshipping

Dropshiping is an innovative way to tackle surplus inventory where you don’t need an inventory to sell products.
How it works:
- Customer place order
- Seller contact supplier
- Supplier packs and ships the product directly to the customer
Benefits:
- Low risk management
- No inventory required
- Simple to implement and beneficial for new business
FIFO and LIFO
FIFO- first in first out. As the term means the first item added to the inventory is supposed to be sold first.
LIFO- last in first out. Here, the most recently added items to inventory are assumed to be the first ones sold or used.
These methods ensure companies don’t end up with surplus stock and inventory is stocked with products with longer shelf life.
Blockchain for Supply
Blockchain can be effective for managing supply and tracking inventory through supply chains. Through analyzing a series of transactions and movements, blockchain is effective in detecting gaps in the system and minimizing conditions that can lead to an excess inventory.
How it works:
- Develop a blockchain-based supply chain management system
- Onboard key suppliers and partners to the blockchain network
- Implement smart contracts for automated inventory management
Benefits:
- Enhanced visibility across the supply chain
- Improved coordination between suppliers and retailers
- Reduced overordering
Platforms for Inventory Sharing
There are platforms where companies can share their inventory stock with partners, that enables them to reduce overall stocks and capital.
Key benefits:
- Reduced overall inventory levels across participating businesses
- Improved ability to meet customer demand
- Lower carrying costs for individual businesses
Implementing Effective Inventory Control
To successfully implement these inventory control techniques, consider the following steps:
- Research and apply effective inventory management practices
- Identify mismanaged areas and make improvement
- Select appropriate inventory control techniques based on business needs
- Invest in inventory management software
- Train staff on new processes and systems
- Continuously monitor and adjust inventory control strategies
Conclusion
Inventory control is pivotal for any business in order to optimize their stock levels, cut down on costs and to meet customer needs. Through the application of these techniques, companies can enhance the overall efficiency of their operations, minimize wastage, and sustain a competent inventory. Through the application of modern technologies, inventory management systems and business intelligence, organizations can improve on the effective control of inventories. Such tools can help achieve real-time inventory monitoring, control the replenishment of the stock, and support decision making processes.





