Introduction to Flea Infestations
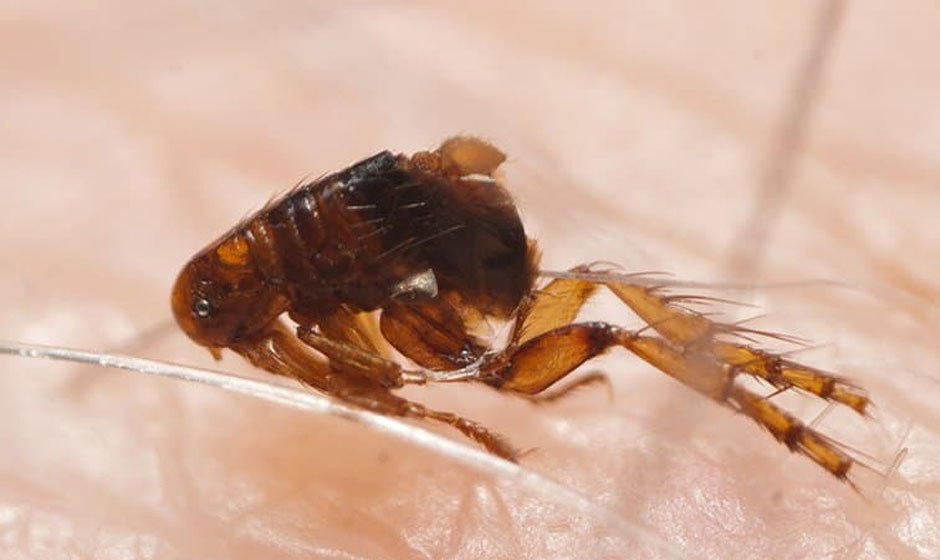
Flea infestations symbolize a prevalent and often underestimated challenge for pet owners and homeowners alike. These minuscule insects readily inhabit environments alongside animals, thriving in warm and humid habitats. Once inside a home, they can rapidly multiply, creating an uncomfortable living situation for humans and pets. Early detection and treatment are critical to stem the tide of a developing flea issue. That’s why understanding how to get rid of pests and prevent reinfestations is invaluable for maintaining a comfortable home environment. Given their tiny size and ability to hide in nooks, fleas can frequently go unnoticed until significant action is required. Fleas present more than a mere annoyance. They can quickly evolve from being just annoying to becoming a serious health concern. Understanding their preferred environments and behaviors allows for more effective management. As with many pest problems, knowledge and preparation are the best defenses against escalation.
The Health Hazards of Flea Infestations
Beyond their irritating bites, fleas carry the potential to pose significant health hazards. The itching and scratching caused by flea bites may result in skin irritations and potentially secondary infections. In more severe cases, fleas are vectors for various illnesses. They transmit severe conditions such as the plague, murine typhus, and flea-borne diseases, including cat scratch fever. Such associations spotlight the importance of effective flea control for comfort and as a critical component of household health and safety strategies. Pets, who often bear the brunt of flea infestations, are particularly susceptible to allergic dermatitis, a hypersensitivity reaction to flea saliva. This condition leads to extreme itching and inflammation and can severely impact the well-being of your furry companions. Thus, regular flea prevention directly promotes overall health for pets and their human companions.
Identifying Signs of a Flea Infestation
While fleas are tiny, the signs of their presence can be apparent if you know what to look for. Pets are frequently the first indicators of flea activity. Scratching, biting, and grooming excessively can suggest an infestation. Look for tiny red or black specks, known as “flea dirt,” around pet resting areas and carpeting. A reddish-brown stain may appear upon dispersing flea dirt on a wet paper towel, indicating blood remnants and confirming flea presence. Fleas are more active in warmer months, making inspections critical to early detection and intervention. Detecting fleas early allows for less complicated interventions. Watch for subtle changes in pet behaviors or the condition of their coat. Regularly check bedding, carpet, and upholstered furniture, employing sticky pads or traps to confirm flea activity.
Preventing Flea Infestations Naturally
Prevention remains the cornerstone of flea control strategies, with natural approaches offering eco-friendly alternatives to chemical treatments. Regular pet grooming, including flea-repellent shampoos, significantly reduces the likelihood of flea infestations. Alongside grooming, frequent vacuuming of floors, furniture, and pet sleeping areas removes flea eggs and larvae, disrupting their lifecycle. Natural repellents, such as diatomaceous earth, a fine powdery substance harmless to pets yet deadly to fleas, can be sprinkled in areas where fleas may inhabit, such as carpets and pet bedding. Essential oils, including lavender and cedarwood, serve as natural flea deterrents. Mixing a few drops into water for a spray or adding these to pet cleansing routines cultivates a flea-resistant environment. Implementing these simple, sustainable practices into routine home care can significantly diminish the potential for infestations.
Understanding Flea Control Methods
Managing fleas effectively involves employing a combination of approaches tailored to the specific infestation scenario. Chemical treatments, such as topical applications and flea sprays, can deliver rapid results but may carry potential hazards if misused. These are generally most effective when targeting an active infestation. In contrast, organic methods prioritize preventative care and establishing environments unfavorable to fleas. Remedies like nematodes and microscopic organisms targeting flea larval stages in the yard can significantly curb infestations outdoors. Each method presents unique advantages and drawbacks. A comprehensive understanding and careful approach can enhance control measures, ensuring safety and efficacy. Considerations regarding pet health, home environment, and personal preferences play into choosing the best methods for any situation.
The Role of Professional Pest Control Services
Professional pest control services embody the frontline solution for extensive or persistent flea issues. When DIY efforts fall short, these services bring specialized knowledge, advanced products, and methods to tackle fleas effectively. Professionals often use integrated pest management strategies considering environmental safety and pest biology, targeting fleas at all lifecycle stages without excess pesticide use. Reputable pest control companies eliminate current infestations and advise on preventative measures and routine checks to maintain a flea-free home. This proactive professional oversight often proves invaluable in achieving long-term flea control.
Flea Control and Public Health
The implications of flea control extend beyond individual homes. Effective flea management contributes to broader public health initiatives. The link between flea control and the prevention of flea-borne diseases underscores the importance of vigilant pest management. Controlling pests like fleas forms a core part of global efforts to reduce disease vectors and protect communities from vector-borne illnesses. Therefore, community education and public health campaigns focusing on flea control can significantly mitigate health issues related to these pests. Sharing resources and knowledge helps foster collective action against infestations, benefitting public well-being.
Conclusion: Maintaining a Flea-Free Environment
A flea-free environment hinges on consistent vigilance, prevention, and timely action. Regardless of the immediate threat level, maintaining routine checks, cleaning, and preventive measures ensures a comfortable living space for all inhabitants. Flea control isn’t simply about addressing infestations as they happen; it’s about cultivating a habitat where fleas are less likely to thrive from the outset. Through informed choices and diligent practices, homeowners can successfully manage and eradicate fleas, safeguarding their homes and loved ones from these pests’ adverse effects.